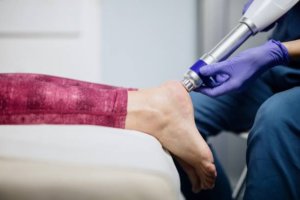
 Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (EWST) is a mechanical therapy that creates local inflammation to promote healing. This therapy creates short bursts of sound waves that create an intense and precise massage to the targeted tissue. Local inflammation is required for all tissues to heal in the body so creating a precise area for the body to send all of its healing elements will speed up the rate of healing. Typically it is recommended to get 6 treatments of shockwave and for optimal results combine it with targeted physical therapy exercises. It’s often used for conditions like tendonitis, plantar fasciitis, and other musculoskeletal injuries that haven’t responded well to traditional treatments.
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (EWST) is a mechanical therapy that creates local inflammation to promote healing. This therapy creates short bursts of sound waves that create an intense and precise massage to the targeted tissue. Local inflammation is required for all tissues to heal in the body so creating a precise area for the body to send all of its healing elements will speed up the rate of healing. Typically it is recommended to get 6 treatments of shockwave and for optimal results combine it with targeted physical therapy exercises. It’s often used for conditions like tendonitis, plantar fasciitis, and other musculoskeletal injuries that haven’t responded well to traditional treatments.
The mechanism of healing is similar to a commonly recommended procedure called PRP (protein-rich protein) to create local inflammation in the injured tissue to promote healing. PRP is a much more invasive and greater expense as it requires a medical professional to extract blood from a patient and use an element called platelets found in the blood to re-inject back into the injured tissue. Shockwave typically accomplishes the same results in the same 6 week time period as PRP for half the cost.
 Common Injuries
Common Injuries
- Achilles Tendonitis
- Quadriceps/Patellar Tendonitis
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Tennis/Golfers Elbow (medial/lateral epicondylitis)
- Rotator Cuff Tendonitis
- Hip bursitis (Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome)
- Hamstring Tendonitis
Who Benefits From Shockwave Therapy?*:
- Athletes
- Active Adults
- Youth Athletes
- Military Veterans
- Women
- People Who Sustained an Injury From an Accident
*Please visit any of our offices to learn more.
“Great sessions with “Dr. Moose” (Dr. Mostafa Kolahdouzan). He employed Shockwave therapy to help me make progress in a problem area I have had for over a decade. Very knowledgeable and personable.” – Evan Miller
For more information:
Aqil A, Siddiqui MR, Solan M, Redfern DJ, Gulati V, Cobb JP. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy is effective in treating chronic plantar fasciitis: a meta-analysis of RCTs. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013 Nov;471(11):3645-52. doi: 10.1007/s11999-013-3132-2. Epub 2013 Jun 28. PMID: 23813184; PMCID: PMC3792262.
Feeney KM. The Effectiveness of Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy for Midportion Achilles Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review. Cureus. 2022 Jul 18;14(7):e26960. doi: 10.7759/cureus.26960. PMID: 35989757; PMCID: PMC9382436.
Halpern BC, Chaudhury S, Rodeo SA. The role of platelet-rich plasma in inducing musculoskeletal tissue healing. HSS J. 2012 Jul;8(2):137-45. doi: 10.1007/s11420-011-9239-7. Epub 2012 Jan 18. PMID: 23874254; PMCID: PMC3715623.
Mani-Babu S, Morrissey D, Waugh C, Screen H, Barton C. The effectiveness of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in lower limb tendinopathy: a systematic review. Am J Sports Med. 2015 Mar;43(3):752-61. doi: 10.1177/0363546514531911. Epub 2014 May 9. PMID: 24817008.
Testa G, Vescio A, Perez S, Consoli A, Costarella L, Sessa G, Pavone V. Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy Treatment in Upper Limb Diseases: A Systematic Review. J Clin Med. 2020 Feb 6;9(2):453. doi: 10.3390/jcm9020453. PMID: 32041301; PMCID: PMC7074316.

